A Quantitative and Qualitative Evaluation of LLM-Based Explainable Fault Localization
Update: April 10, 2025
先前的方法缺少对suggested locations的解释,本文提出AutoFL,“prompts an LLM to use function calls to navigate a repository”。
Contributions
- 方法:使用LLM驱动的代码相关信息检索,使用LLM完成漏洞定位及解释;
- 漏洞定位性能:AutoFL在2个真实世界bug benchmarks上较baselines表现更好;
- 定位解释性能:对超过半数的漏洞可以给出准确解释,开发者对AutoFL生成的解释持积极态度。
Approach
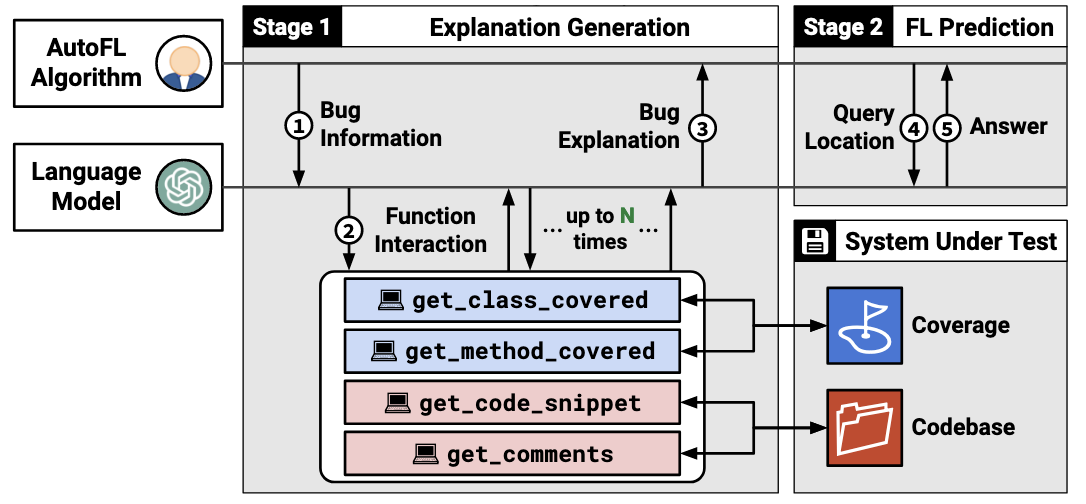
目标: generate logical flow from the root cause to the failure
- method-level fault location
stage 1: 分析root cause
(1) prompt (bug information): failing test + 相关函数描述
(2) retrieve (function interaction): LLM驱动的信息获取
- 使用LLM决定提取哪些信息,以及是否进行explanation。
- 一共有4种信息:class-level coverage information, method-level coverage information, method code, method comments.
- 其中,method code和method comments需要LLM提取的method signatures作为输入。
(3) explain: LLM根据提取的信息生成root cause explanation
stage 2: 获取fault location输出
(4) predict: LLM预测具体fault method
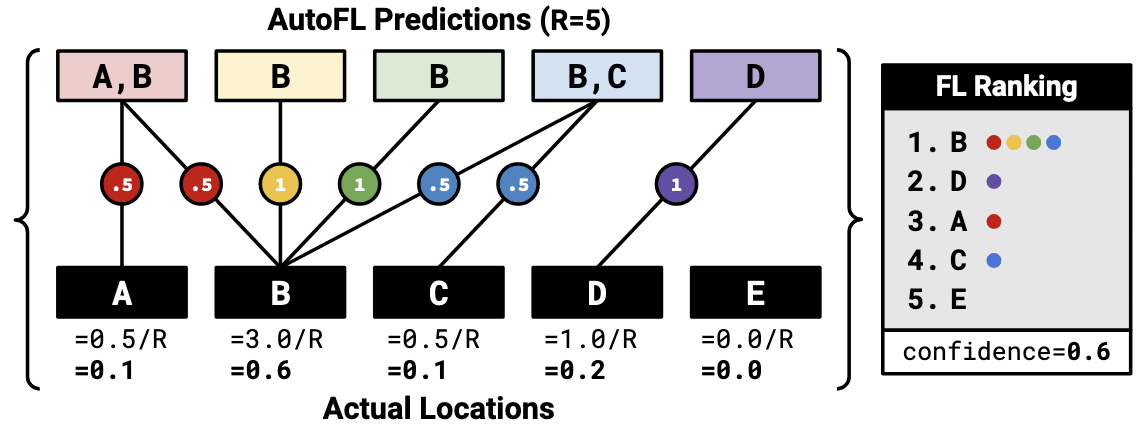
(5) ranking: 使用LLM多次预测fault method,计算score对method排序,并以最高score作为confidence。
\[\text{score}(m) = \frac{1}{R} \sum_{k=1}^{R} \left( \frac{1}{|r_k|} \cdot [ m \in r_k ] \right)\]其中,$r_k$ 表示第k次预测中,预测得到的fault method总数;R为总预测次数。
Related work
- Xueying Du, Yiling Lou, Mingwei Liu, Xin Peng, and Tianyong Yang. 2023. KG4CraSolver: Recommending Crash Solutions via Knowledge Graph. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM Joint European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering (ESEC/FSE ’23). ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/3611643.3616317